RAD seq
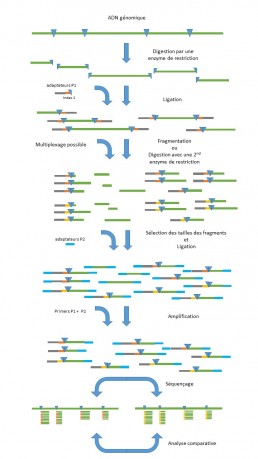
RAD seq (Restriction-site Associated DNA sequencing) represents an alternative to whole genome NGS sequencing for the detection, without a preconceived notion, of SNPs and indel variations in DNA. This method consists in the targeted sequencing of regions adjacent to common restriction sites distributed throughout the genome. The use of several restriction enzymes will increase the coverage of the genome, without the need for a reference genome.
After digestion by a restriction enzyme, a first ligation allows to add to the DNA fragments a P1 adapter, complementary to the restriction site and barcoded for sample identification. P1 also contains the sites of the amplification and sequencing primers. The next step is a mechanical fragmentation associated with a size selection of the fragments according to sequencing requirements. For a better adjustment of the size selection step, the fragmentation can be replaced by digestion with a second restriction enzyme (ddRADseq). The P2 adapter is then ligated to the selected fragments. PCR with the amplification primers P1 and P2 will allow amplification only of the fragments carrying the adapters P1 and P2 at their ends (see Figure).
RADseq is a powerful population genomics tool applicable to comparative (Perry EB et al. 2017) and evolutionary analyses in the context of organisms that do not have an available reference genome (Andrews et al. 2016).
Platforms to contact for RAD seq projets