« Long Reads ONT » Sequencing
The sequencing technology proposed by ONT (Oxford Nanopore Technologies) is based on the detection of a differences in electic current during the passage of a single linear molecule through a biological nanopore anchored in a synthetic membrane. The nanopore is sensor for the ion flow that varies according to the steric hindrance of the compound passing through it, enabling the identification of the sequence of a DNA strand over a long length (up to several Mb) whatever its composition in repeated elements, GC-rich or methylated regions. This technique is effective for de novo sequencing or detection of structural variants or to resolve missing heritability elements (Logsdon GA et al. 2020).
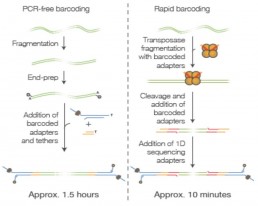
To generate long or very long reads (>100kb), a high molecular weight DNA extraction method should be performed. Several methods are available for library preparation. The first step is mechanical (g-tube) or enzymatic (transposase) fragmentation. The indexed fragments are ligated with adapters carrying a “motor” complex that modulates the speed of passage of the DNA strand through the nanopore and a “tether” sequence that facilitates the convergence of the DNA strands towards the entrance of a pore.